Binomial Trees
When pricing options, we don’t know whether the price will go up or down. This simple model captures that uncertainty.
Monte Carlo Simulation
The behaviour of a stock price is like a random walk. Let’s simulate a very large number of these to predict our option price.
Black Scholes equation
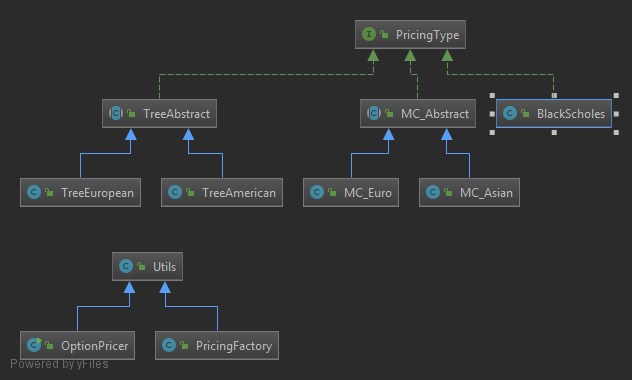
Class Diagram
OptionPricer.java
Input
The main class is OptionPricer.java, which reads pricingtypes.txt.
This file contains the following strings:
American Binomial Tree
Asian Monte Carlo
European Binomial Tree
European Monte Carlo
Black Scholes
Body
public class OptionPricer extends Utils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] Name = readTxt("pricingtypes.txt");
PricingFactory factory = new PricingFactory();
for (String str : Name) {
PricingType pricing = factory.getPricingType(str);
double call = pricing.getCall();
double put = pricing.getPut();
System.out.printf("%s\n\tCall:%.14f\n\tPut:%.14f\n", str, call, put);
}
}
}
Interface
This is used by PricingFactory.java to construct the appropriate concrete class from the interface PricingType.java class.
Classes that implement this interface are:
- BlackScholes
- MC_Abstract
- TreeAbstract
Methods
PricingType.java presecribes the following methods to be implemented:
double getCall()
double getPut()
Abstract Classes
Monte Carlo
In certain cases, we are concerned with comparing the different type of pay-offs that can be utilised under each pricing method. For instance, when pricing via Monte Carlo, we are able to compare the difference in option prices that result from considering both Asian and European pay-off.
- MC_Abstract.java
- MC_Asian.java
- MC_Euro.java
As such, we have an abstract class MC_Abstract.java which is extended by MC_Asian.java and MC_Euro.java.
Both these concrete classes must define their own implementations of the following method:
public double simulateRandomwalk (int N, double S0, double dt, double interest, double sigma)
Binomial Tree
We have a similar relationship with the abstract class TreeAbstract.java and its concrete classes.
- TreeAbstract.java
- TreeAmerican.java
- TreeEuropean.java
The difference between an American and European option is that an American put can be exercised at any time up to maturity. The European put can only be exercised at maturity. There is no difference between American and European calls.
As such, the concrete classes must implement their own version of the following method:
public double setPut(double[][] stockPrice, double strike, double interest, double p, double dt, int T)
Inputs
In addition to pricingtypes.txt, we have a number of input .txt files.
- Binomial.txt
- BlackScholes.txt
- MonteCarlo.txt
These files contain the following:
stock,115
strike,80
volatility,0.48
interest,0.07
timehorizon,0.5
Each file contain identical data. But the user is free to modify the data for each implmentation.
On each line is a comma separated key-value-pair such that this data is mapped accordingly: HashMap<String, Double>.
This allows for the following convenience:
double stock = hashMap.get("stock");
double strike = hashMap.get("strike");
double volatility = hashMap.get("volatility");
double interest = hashMap.get("interest");
double timehorizon = hashMap.get("timehorizon");


